16 February 2022


Sébastien de Rosbo,
research manager, BuddeComm
During the last few years Libya has struggled to rebuild its economy and infrastructure following disruption caused by the civil war and the subsequent political unrest. Much of the telecom infrastructure was destroyed or stolen following the 2011 disturbances, including about a quarter of the country’s mobile tower sites. For many years reconstruction efforts were stymied by political and military disturbances which affected much of the country. During the decade during which there were two opposing administrations, based in Tripoli and Tobruk, there was no consensus as to how to rebuild infrastructure on a national scale despite numerous attempts to reach a political solution. Some change is anticipated following the formation of a UN-brokered Government of National Unity in March 2021, though this was an interim measure pending the anticipated presidential and legislative elections set for early 2022.
Despite the political deadlock, there has been some progress made in rebuilding telecom infrastructure. The MNOs have cooperated to extend the reach of LTE services in the south of the country. This has been facilitated by the newly achieved political stability, since the various warring factions had previously targeted telecom towers.
The mobile market is supported by some of the lowest tariffs on the continent. Opportunities remain in the broadband sector where market penetration is still relatively low. To stimulate take-up of services, the regulator in mid-2020 imposed a 50% reduction in internet subscription charges. As for mobile broadband, LTE services have only a limited reach and thus the development of this sector has been slow. A limited 5G service was made available in November 2019.
BuddeComm notes that the outbreak of the Coronavirus continues to have a significant impact on production and supply chains globally. During the coming year the telecoms sector to various degrees is likely to experience a downturn in mobile device production, while it may also be difficult for network operators to manage workflows when maintaining and upgrading existing infrastructure. Overall progress towards 5G may be postponed or slowed down in some countries.
On the consumer side, spending on telecoms services and devices is under pressure from the financial effect of large-scale job losses and the consequent restriction on disposable incomes. However, the crucial nature of telecom services, both for general communication as well as a tool for home-working, will offset such pressures. In many markets the net effect should be a steady though reduced increase in subscriber growth.
Although it is challenging to predict and interpret the long-term impacts of the crisis as it develops, these have been acknowledged in the industry forecasts contained in this report.
The report also covers the responses of the telecom operators as well as government agencies and regulators as they react to the crisis to ensure that citizens can continue to make optimum use of telecom services. This can be reflected in subsidy schemes and the promotion of tele-health and tele-education, among other solutions.
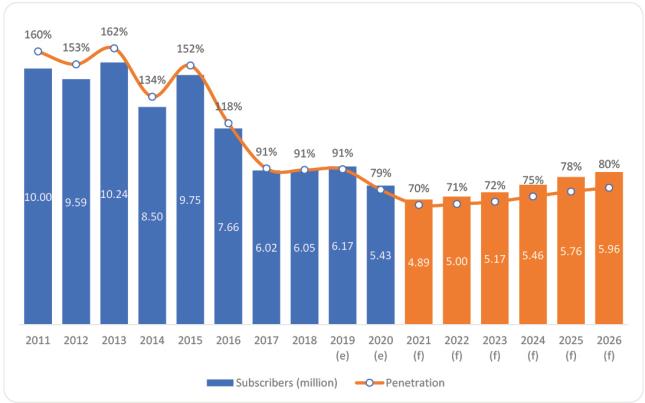
Table 2 – Growth in the number of mobile subscribers and penetration – 2011 – 2026
| Year | Subscribers (million) | Penetration |
| 2011 | 10.000 | 160.1% |
| 2012 | 9.587 | 152.5% |
| 2013 | 10.235 | 161.9% |
| 2014 | 8.497 | 133.6% |
| 2015 | 9.747 | 151.9% |
| 2016 | 7.660 | 118.0% |
| 2017 | 6.020 | 91.5% |
| 2018 | 6.050 | 90.6% |
| 2019 (e) | 6.170 | 91.0% |
| 2020 (e) | 5.430 | 79.0% |
| 2021 (e) | 4.887 | 70.1% |
| 2022 (f) | 4.999 | 70.7% |
| 2023 (f) | 5.169 | 72.0% |
| 2024 (f) | 5.458 | 75.1% |
| 2025 (f) | 5.759 | 78.0% |
| 2026 (f) | 5.960 | 80.2% |
Source: BuddeComm based on ITU data
Key developments:
- Hatif Libya contracts Infinera to provide an optical transport network to unserved areas of the country;
- Silphium submarine cable linking Derna with Greece is again brought on stream;
- LPTIC contracts Ericsson to maintain and develop the country’s telecom networks and infrastructure;
- Government orders 50% reduction in internet subscription fees;
- Al-Madar extends LTE service to Benghazi and Misurata;
- LTT launches LTE-based fixed broadband network;
- LPTIC signs $80 million contract with Arabsat to provide satellite broadband services;
- Italy-Libya cable upgraded to support 100Gb/s technology;
- Report update includes Telecom Maturity Index charts and analyses, assessment of the global impact of Covid-19 on the telecoms sector, recent market developments.
Chart 10 – Growth in the number of mobile subscribers and penetration – 2011 – 2026
Source: BuddeComm based on ITU data www.budde.com.au






